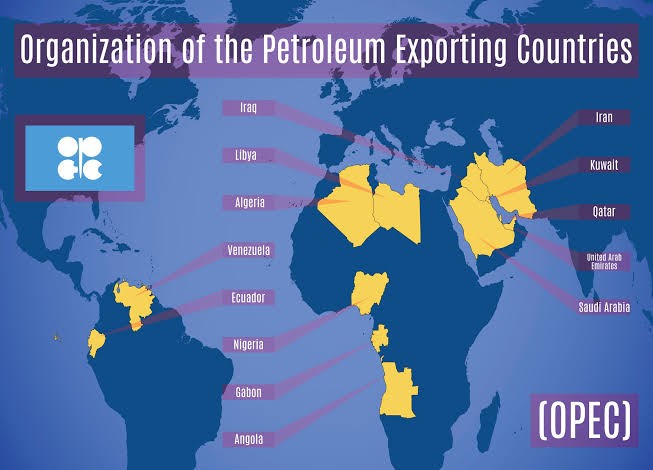
The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries, commonly known as OPEC, stands as one of the most influential and impactful organizations in the realm of global energy. Established in 1960, OPEC comprises 13 member countries, primarily located in the Middle East, Africa, and South America. This essay will delve into the history, structure, significance, challenges, and the evolving role of OPEC in the global energy landscape.
History and Formation of OPEC
OPEC emerged against the backdrop of a changing global oil market. In the mid-20th century, Western oil companies dominated oil production and pricing, leaving oil-rich nations with little control over their resources. Frustrated by this situation and seeking greater sovereignty over their oil reserves, five founding members—Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela—established OPEC in Baghdad on September 14, 1960. The organization aimed to coordinate and unify their petroleum policies, thereby asserting more control over oil production and pricing.

Structure and Objectives of OPEC
OPEC operates as a collective intergovernmental organization, with member countries working together to influence oil prices and regulate production levels. The decisions made within OPEC are primarily based on achieving stable oil markets, securing fair prices for producers, and ensuring a steady supply of oil to consumers worldwide. The organization is governed by the Conference, which consists of representatives from each member nation. The Conference meets biannually to discuss and decide on various oil-related issues, including production quotas, pricing strategies, and market stabilization measures.
Also Read :-what is G7 ?
Significance and Influence of OPEC
The significance of OPEC lies in its control over a substantial portion of the world’s oil reserves and production. Member nations collectively hold vast quantities of crude oil, granting OPEC significant leverage in influencing global oil prices. The organization’s decisions on production levels and pricing have a direct impact on the world economy, energy markets, and geopolitical dynamics.
OPEC’s actions have historically led to fluctuations in oil prices, affecting industries, economies, and consumers globally. Its ability to regulate output and pricing can influence inflation rates, trade balances, and the economic well-being of both oil-exporting and oil-importing nations.
Challenges Faced by OPEC
Despite its considerable influence, OPEC faces several challenges that impact its effectiveness and cohesion. One such challenge is the diversity among member nations regarding production capacities, economic needs, and geopolitical interests. Balancing the interests of countries with varying levels of oil reserves and economic reliance on oil revenues poses a constant challenge for OPEC’s decision-making processes.
Another significant challenge is the changing dynamics of the global energy landscape. The rise of alternative energy sources, such as renewable energy and advancements in technology, has contributed to shifting preferences away from fossil fuels. This shift presents OPEC with the challenge of adapting to a changing market while also ensuring the relevance of its policies in an increasingly diversified energy mix.
Evolving Role of OPEC in a Changing Energy Landscape
OPEC has responded to these challenges by adjusting its strategies and policies to align with the evolving global energy scenario. Recognizing the growing importance of renewable energy and climate change concerns, some member nations have begun diversifying their economies and investing in renewable energy projects. OPEC itself has acknowledged the need to address environmental concerns and has expressed willingness to collaborate with other stakeholders to tackle climate change.
Moreover, OPEC has sought to engage with non-OPEC oil-producing countries, such as Russia and other significant oil producers, in coordinated efforts to stabilize oil markets through initiatives like the OPEC+ alliance. This partnership aims to manage oil production collectively to maintain market stability and address supply-demand imbalances.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries holds a crucial position in the global energy landscape, exerting substantial influence over oil markets and prices. Its history reflects the quest for sovereignty and control over natural resources among oil-rich nations. Despite facing challenges such as divergent interests among member nations and the shifting energy landscape, OPEC continues to adapt and evolve its strategies to maintain its relevance.
As the world moves towards a more diversified energy future, OPEC’s role in ensuring stability in oil markets and its willingness to collaborate with other stakeholders in addressing global energy challenges will be pivotal. How OPEC navigates these challenges and adapts to the changing dynamics of the energy landscape will determine its continued significance in the global energy arena.
OPEC remains a pivotal player in the global energy landscape, navigating challenges and adapting to the changing dynamics of the market. Its ability to evolve its strategies, embrace innovation, and collaborate across borders will determine its ongoing relevance and influence in shaping the future of the energy industry. As the world moves towards a more sustainable and diversified energy future, OPEC’s role in facilitating this transition will be critical.